
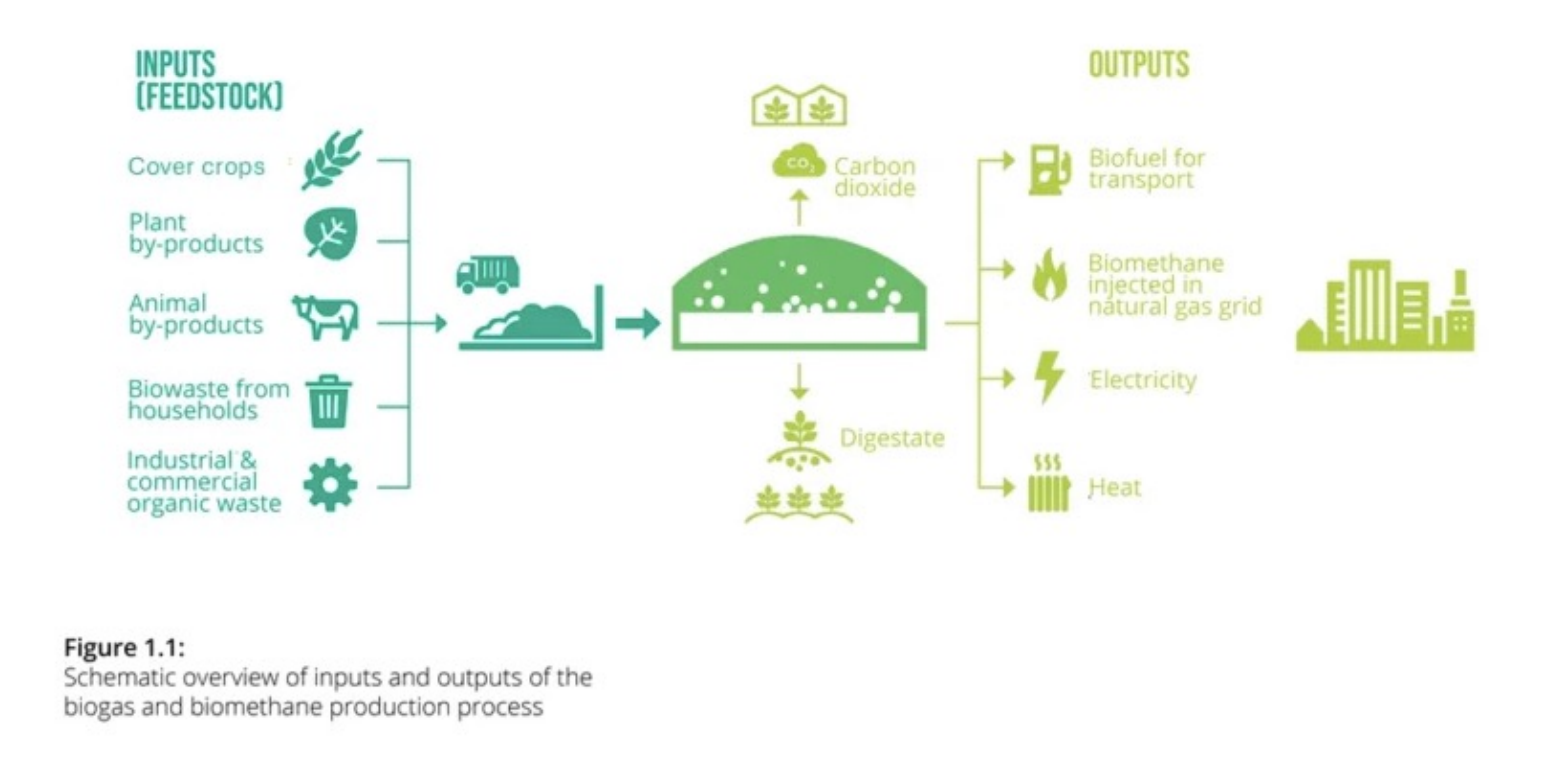
CBG BASICS
CBG or bio-CNG is primarily methane (>95 % ) with a calorific value of 47–52 MJ/kg and can be used as a substitute for fossil fuels like natural gas, petrol and diesel.
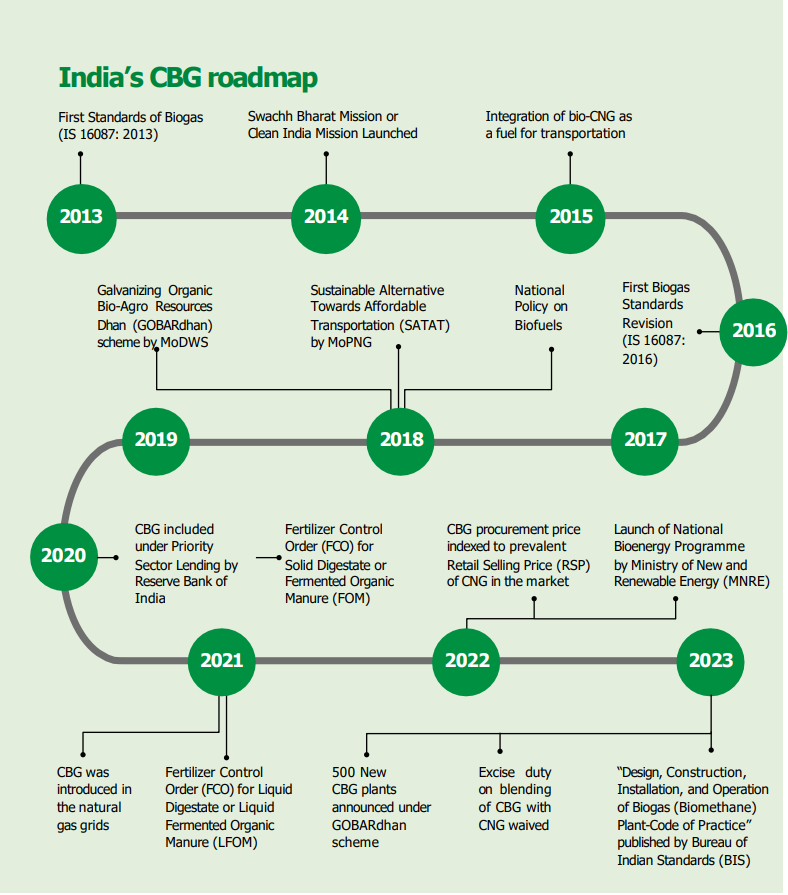
India’s CBG industry got a major push by the introduction of the Sustainable Alternative towards Affordable Transportation (SATAT) scheme by the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas in 2018.
As of March 2023, 58 CBG plants have been operationalized in India, and a letter of intent for setting up similar plants has been issued to 3,694 prospective investors.
Difference between Biogas and Compressed Biogas (CBG)
The main difference between biogas and compressed biogas (CBG) is in their composition and properties (see Table 2: Composition of biogas and CBG). Biogas is a mixture of gases, primarily methane and carbon dioxide, produced by the breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen. It also contains small amounts of other gases such as hydrogen, nitrogen and hydrogen sulphide.
On the other hand, bio-CNG or CBG is a purified form of biogas that has been compressed to high pressure and has undergone further processing to remove impurities such as carbon dioxide, moisture and hydrogen sulphide. This results in a gas that is primarily methane, with a methane content of at least 96 per cent, and can be used as a substitute for fossil fuels like natural gas and diesel.
Table 2: Composition of biogas and CBG
| Composition | Raw biogas | Bio-CNG/CBG |
|---|---|---|
| Methane | 55–65% | >95% |
| Carbon dioxide | 30–40% | <4% |
| Hydrogen sulphide | 0.1–4% | <16 ppm |
| Nitrogen | 0% | <0.5% |
| Oxygen | 0.1–2% | <0.5% |
| Moisture | 1–2% | 0% |
| Calorific value | 19.5 MJ/kg | 47–52 MJ/kg |
How Biogas compares with other Fuels
The energy content of biogas is compared to other fuels in terms of its heating value, which is a measure of the amount of energy released when the fuel is burned (see Table 3: Quantity of different fuels required to produce heating value equivalent to 1 m3 of biogas). The heating value of biogas depends on its composition, particularly its methane content, which typically ranges from 50–70 per cent. The higher the methane content, the higher the heating value of the biogas.
Calirific Value (MJ/m3)
Table 3 :Quantity of different fuels required to produce heating value equivalent to 1m3 of biogas
| Name of the fuel | Equivalent quantity to 1m3 of biogas |
|---|---|
| Kerosene | 0.62 l |
| Firewood | 3.50 kg |
| Cattle dung cake | 12.3 kg |
| Charcoal | 1.46 kg |
| Furnace oil | 0.40 l |
| Electricity | 1.25 kW |
| LPG | 0.43 kg |
| Diesel | 0.52 l |
| Coal | 1.6 kg |
Installed capacity and commissioned plants
According to the information available on the Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation (SATAT) portal and MNRE, 58 CBG plants have been commissioned in India, and 3,694 potential investors have been issued a letter of intent (LOI) for setting up similar plants as of March 2023. Moreover, as of that date, approximately 9,019 tonnes of CBG has been sold.
